Lower limb injury management in children

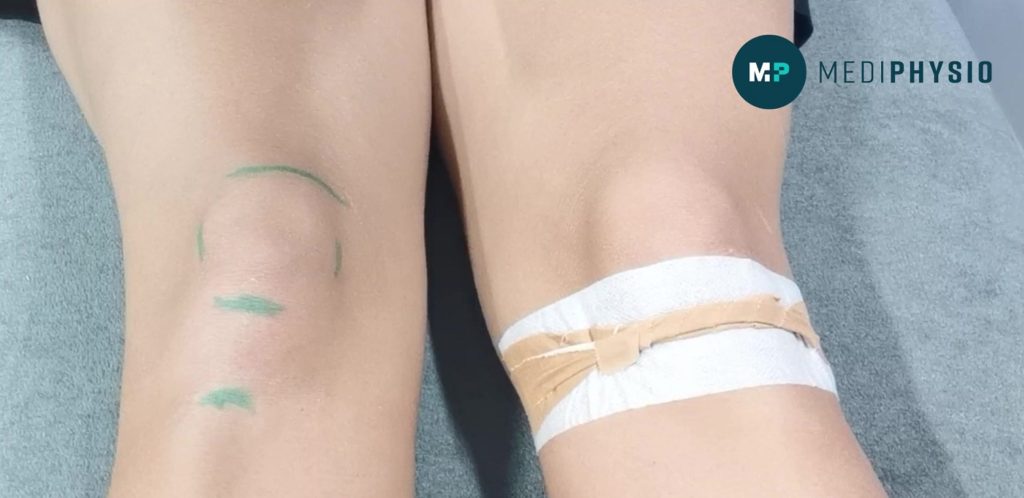
Following on from Lower limb injuries in children. Here we talk about a physios role in helping our active youths return to exercise safely. At Mediphysio we work with children as they go through their varying activity levels, growth spurts and potential injuries. Featured above and at the end of this blog are some common taping techniques we use to unload around the knee.
How do physios help our younger patients differently?
Health professionals have a critical role in guiding both young patients and their parents in the appropriate management of not just their symptoms, but also their developing views on the impact that physical activity can have on their lives.
It is well known that many musculoskeletal pathologies that affect pubescent youths can cause significant pain and functional limitation for long periods of time, such as up to 24 months for OSD
Wilson & Rodenberg 2011
This happens to be the time when there is critical development for adolescents both physically and psychosocially. Sources of chronic pain and activity limitation can lead to reduced participation in sports, or even withdrawal altogether.
Reeves & Dean 2006
Research continues to indicate that some youth specific conditions, such as OSD and Sever’s lesion are self-limiting conditions. Appropriate education to patients and their parents on prognosis, relative rest, and load management can drastically alter their sports participation until at least the end of puberty.

Don’t always have to stop activity, modification is best!
Considering the rise in childhood obesity, encouraging continued physical activity should always be a priority. Long term rest is often unnecessary for these particular conditions and can result in missed opportunity for psychosocial and complex motor development that can occur during sport and activity with peers. As physios we advocate for our patients to proactively manage their condition.
What do physios do to help with your child’s recovery?
- Distinguish between adult and youth injuries for similar mechanisms of injury
- Exclude more serious pathologies, e.g Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis
- Educate both parents and the children about the condition and management plan. Children obviously require different language and motivations to participate in treatment plans
- Language selection based on cognitive age. Children may take expressions literally; can promote castastrophising and fear avoidance
- Promote load management or short periods of relative rest over complete cessation of activity
PHYSIOTHERAPY MANAGEMENT
Education on pathology, anatomy and biomechanics of the affected region.
Education regarding prognosis, and impact on participation
(e.g OSD - self limiting condition)
Appropriate Manual Therapy
- soft tissue release
- joint mobilisation
- taping
- bracing
Thorough exercise program development related to age of patient
* stretching - can they define stretch vs pain?
* neuromuscular control (coordination)
* strengthening
Develop self-management strategies
- Rest vs Load management
- Identification of triggers e.g jumping
CHECK OUT THIS COMMON TAPING TECHNIQUE WE USE TO UNLOAD THE KNEE
If you are requiring some guidance as to how better help your child stay active. Contact us and make an appointment to today!


Sorry, comments are closed for this post.